Best VNC Scanner Tools to Use in 2025 – Find, Secure & Manage Remote Connections

If you want to scan VNC accurately, you know that simply checking for an open port 5900 isn’t enough. VNC servers require an open port for connections—unless you use a reverse-connection method. Many scanners assume that an open port means a VNC server is active, but this often leads to false positives.
To help you find the most reliable solutions, we tested multiple tools and will show you the best options for accurately detecting active VNC servers—not just open ports.
Best VNC Scanner Tools
| Feature | VNC Neighborhood | Scan4VNC | UltraVNC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | A free VNC server TCP scanner. | A remote diagnostics and management tool for administrators of small, heterogeneous LANs. | A powerful, easy-to-use, free remote PC access software that can display the screen of another computer on your own screen. |
| Platform | Windows | Windows | Windows |
| Port Scanning | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| VNC Detection | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Additional Features | – | Remote diagnostics and management. | Remote desktop access, file transfer, chat. |
1. VNC Neighborhood
VNC Neighborhood is able to locate VNC servers and also provide an easy way to launch the viewer and connect to the servers. Although VNC Neighborhood was last updated 6 years ago, but it worked perfectly on Windows 7 32-bit. We previously mentioned that most port scanner assumes that a service is running based on the port number but VNC Neighborhood seems to have a signature detection where it can detect if the open port is being used by a VNC server.
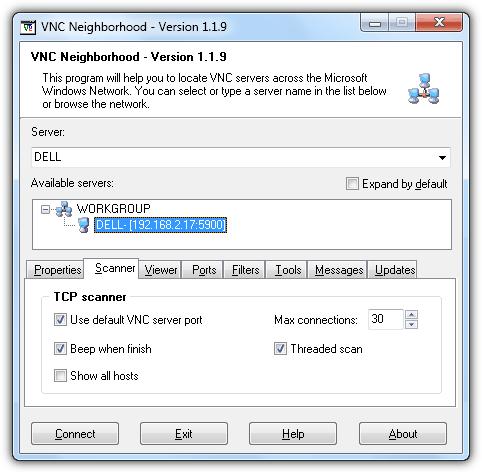
As a test, we opened port 5900 using a program called Local TCP Port Opener to simulate the VNC service. VNC Neighborhood did not find anything even though the port 5900 was opened by Local TCP Port Opener. Next, we tried running 3 different VNC servers (RealVNC, TightVNC and UltraVNC) and amazingly VNC Neighborhood detected all 3 servers.
VNC Neighborhood can be a bit tricky to use because you cannot find a scan button on the program’s interface. In fact it is very easy to start a scan. VNC Neighborhood will automatically detect your network and all you need to do is double click on the WORKGROUP or right click and select Refresh domain on the available servers box. At the Scanner tab, you can configure if you want to only scan the default VNC port, beep notification when finished scanning, threaded and maximum connections. If you unchecked the “Use default VNC server port”, you will need to manually add the port numbers that you want to scan at the Ports tab. To easily connect to the detected VNC servers, you will need to specify the Viewer path and also the password before you can connect to the servers by double clicking on the computer name displayed in the list.
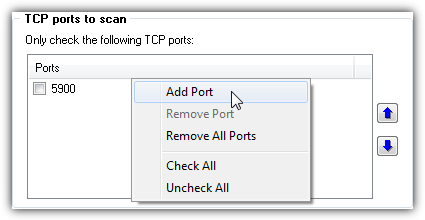
VNC Neighborhood is very fast in scanning and free but it has its limitation where it can only scan your local network and you cannot check a port range.
Scan4VNC
Scan4VNC is also another very old tool that is still capable of detecting VNC servers. It is actually a Windows Scripting Host script and requires a registration of the provided kvbWinsockLib.Dll file with regsvr32.exe in Windows. To register the kvbWinsockLib.Dll file, double click on it, and click the Browse button on the Open with window. Browse to C:\Windows\System32\, select regsvr32.exe and click Open. Click the OK button and you will get the message “DllRegisterServer in …. succeeded”. Now double click on scan4vnc.wsf to run Scan4VNC.
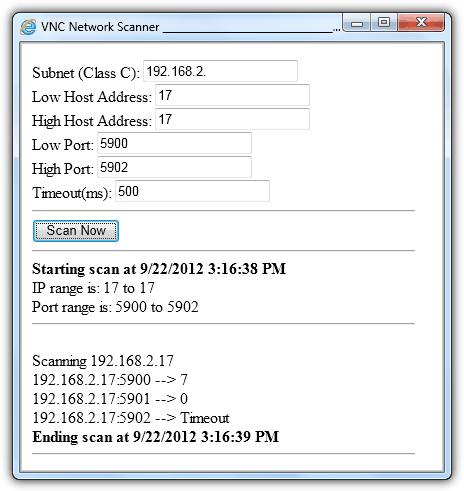
Scan4VNC is more flexible where you can scan the whole subnet, providing the IP and port range. Once you’ve entered all the required information, click the Scan Now button to start scanning. You should take note of the scan result because they are not obvious. If you see a result of 0, it means that the port is open, timeout means that the port is closed and the most important result is 7 which means a VNC server is running on that port.
Scan4VNC is free and successfully tested on Windows 7 32-bit.
3. UltraVNC
UltraVNC is a powerful remote desktop access tool that also includes VNC scanning capabilities. Unlike simple scanners, UltraVNC allows users to both detect and connect to VNC servers seamlessly. It supports Windows operating systems and provides additional features such as file transfer, chat, and authentication for secure remote access.
To test UltraVNC’s scanning ability, we configured a network with multiple VNC servers, including RealVNC, TightVNC, and UltraVNC itself. The built-in scanner successfully detected all active VNC servers and allowed instant connections via its integrated viewer. Unlike VNC Neighborhood, UltraVNC does not rely solely on port scanning but verifies the presence of a VNC server before listing it as available.
UltraVNC is easy to use and provides a user-friendly interface for both beginners and advanced users. The program’s main advantage is its dual functionality—acting as both a scanner and a full-featured VNC client for remote access. However, its scanning features are limited to detecting VNC servers that use standard authentication and may not work as effectively for servers with additional security layers.
UltraVNC is free to use and works well on modern Windows systems.
In conclusion, selecting the right VNC scanner depends on your needs, whether it’s VNC Neighborhood for speed, Scan4VNC for flexibility, or UltraVNC for remote access features.
For further insights into remote management, check out these related guides: remotely enable Windows Remote Desktop, transfer files during remote sessions, access a remote computer without port forwarding, and learn how to manage multiple network connections with TCP/IP Manager.



User forum
0 messages